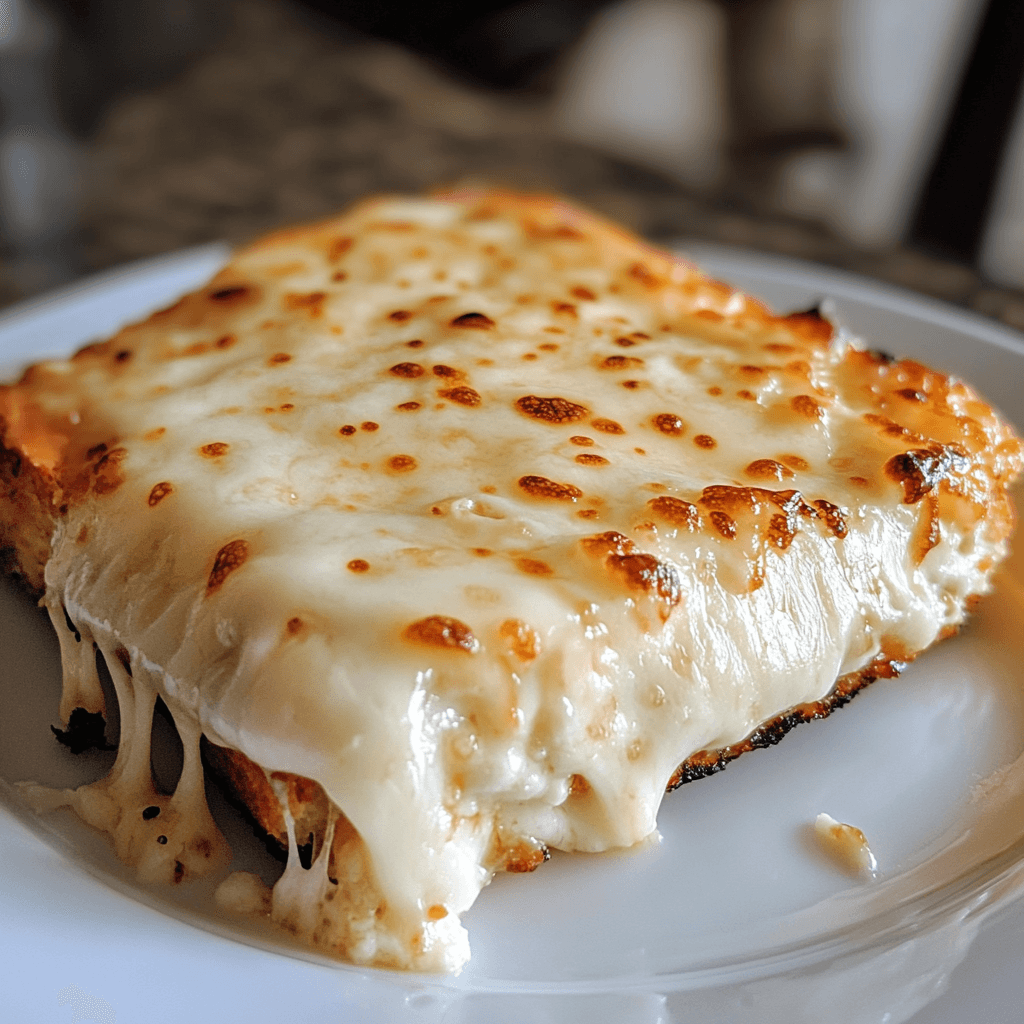
Introduction: Does Cottage Cheese Melt Like Cheese?
Many people assume that all cheeses melt when heated, creating a smooth, gooey texture like cheddar or mozzarella. However, not all cheeses behave the same way. Does Cottage Cheese Melt Like Cheese? The short answer is no—cottage cheese does not melt in the same way as traditional melting cheeses.
The way cheese melts depends on fat content, moisture levels, and protein structure. Some cheeses turn into a creamy, stringy consistency, while others, like cottage cheese, retain their curds when heated. In this guide, we’ll explore why Does Cottage Cheese Melt Like Cheese?, the science behind cheese melting, and how to use cottage cheese in cooked dishes.
Understanding Cheese Melting: What Makes Cheese Melt?
To answer the question, Does Cottage Cheese Melt Like Cheese?, it’s important to explore why some cheeses melt while others don’t. The melting process depends on three key factors:
Fat Content
- Cheeses with higher fat content (such as cheddar or gouda) melt more smoothly because the fat helps break down the protein structure.
- Cottage cheese is naturally low in fat, which means it lacks the necessary fat to create a smooth, melted consistency.
Moisture Levels
- High-moisture cheeses like mozzarella and brie melt easily because the moisture turns to steam, softening the cheese.
- Cottage cheese contains a lot of moisture, but it’s stored within separate curds. Instead of melting, the curds simply release water and become firmer.
Protein Structure
- The protein structure in cheese plays a big role in melting.
- Cheeses like Swiss and provolone have a protein structure that allows them to break down into a stretchy, gooey texture.
- Cottage cheese, on the other hand, is made by curdling milk with acid. This process creates curds that don’t break down when heated, meaning they retain their shape rather than melting into a smooth consistency.
Now that we understand why some cheeses melt while others don’t, let’s take a closer look at Does Cottage Cheese Melt Like Cheese? and how its composition affects its melting behavior. Cottage Cheese in Cooking – Does Cottage Cheese Melt Like Cheese?
What is Cottage Cheese? A Look at Its Composition
To fully answer the question “Does Cottage Cheese Melt Like Cheese?”, we need to examine what cottage cheese is made of. Cottage cheese is a fresh, unripened cheese made from milk curds. It has a mild flavor and a slightly grainy texture, making it a popular choice for healthy meals and protein-packed dishes. But what exactly makes cottage cheese so different from traditional melting cheeses?
Ingredients in Cottage Cheese
Curds: Small, lumpy pieces of cheese that give cottage cheese its unique texture.
Whey: The liquid portion of milk, which is not fully removed from the curds.
Moisture: Cottage cheese has a high moisture content, but it does not contribute to melting.
Acid or Enzymes: Used to curdle the milk and form the cheese.
How Cottage Cheese Differs from Melting Cheeses
- Unlike cheddar or mozzarella, which undergo aging and processing to create a smooth texture, cottage cheese remains fresh and retains its curds.
- The acidic nature of cottage cheese keeps the curds firm even when heated, preventing it from melting like traditional cheese.
- Low-fat cottage cheese has even less fat than full-fat versions, making it even more resistant to melting.
Does Cottage Cheese Melt Like Cheese Such as Cheddar or Mozzarella?
Direct Comparison of Melting Properties
| Cheese Type | Melts Smoothly? | Texture When Heated |
|---|---|---|
| Cheddar | ✅ Yes | Gooey, creamy |
| Mozzarella | ✅ Yes | Stretchy, stringy |
| Gouda | ✅ Yes | Soft, smooth |
| Cottage Cheese | ❌ No | Firmer curds, releases liquid |
Why Cottage Cheese Doesn’t Melt Like Cheddar or Mozzarella
- Curd Structure: The curds in cottage cheese do not break down under heat. Instead, they become firmer as moisture evaporates.
- Lack of Fat: Cottage cheese is lower in fat than melting cheeses, meaning it lacks the creamy consistency needed for a smooth melt.
- High Moisture Content: Instead of melting, cottage cheese releases water when heated, which can make dishes watery.
What Happens When You Heat Cottage Cheese?
Instead of turning into a gooey, melted texture like cheddar or mozzarella, cottage cheese firms up and separates. Here’s what to expect:
In sauces: The curds remain visible, giving the dish a grainy texture.
In baking: The curds hold their shape but may soften slightly.
In hot dishes: The whey separates, and the cheese becomes firmer rather than melting.
Storing & Refrigerating Cheese-Based Foods – Does Cottage Cheese Flatbread Need to Be Refrigerated?
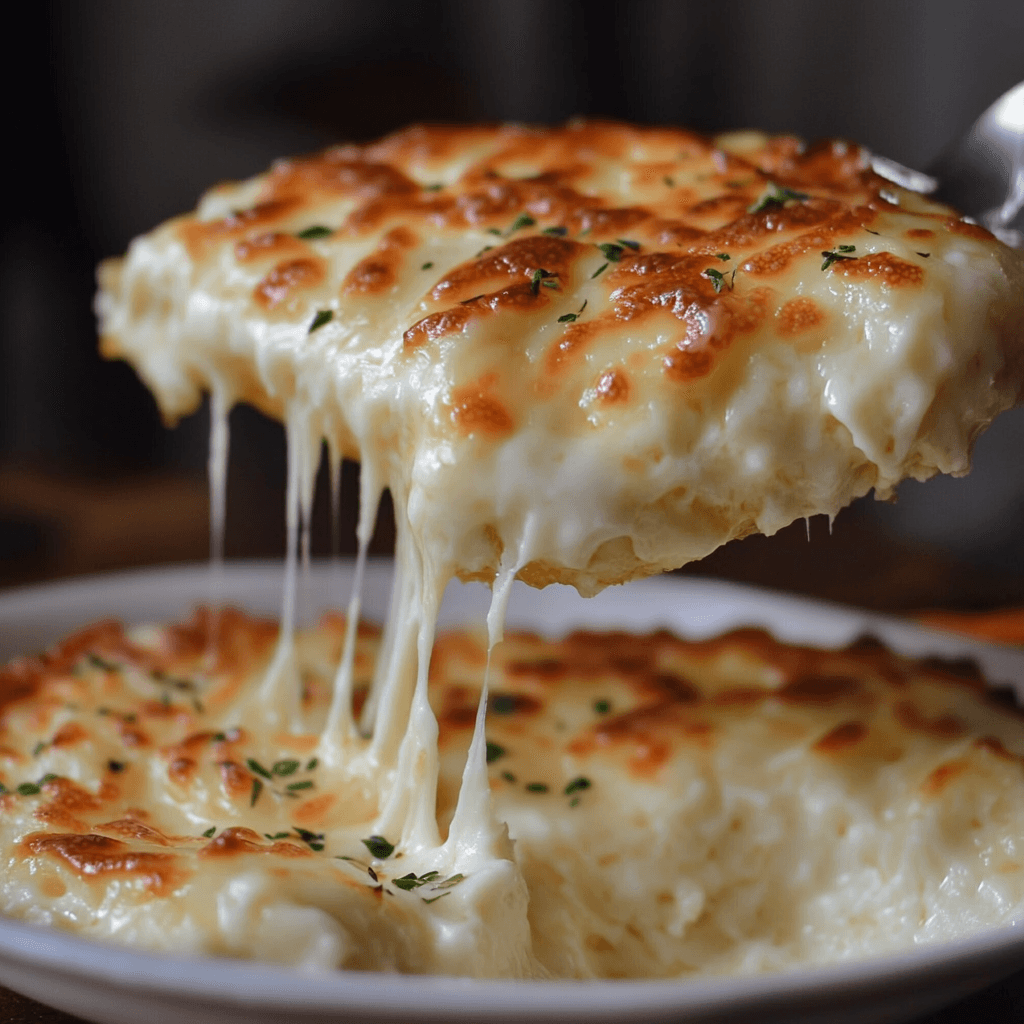

Why Doesn’t Cottage Cheese Melt Like Cheese?
Many cheeses, such as cheddar and mozzarella, melt into a smooth, gooey texture when heated. However, does cottage cheese melt like cheese in the same way? No, and this section explains why.
The Role of High Moisture and Low Fat
Cottage cheese has a high moisture content and low fat percentage, making it behave differently when exposed to heat.
- High Moisture Content: The curds in cottage cheese contain a large amount of water. When heated, this moisture evaporates rather than helping the cheese melt. Instead of becoming creamy, the curds dry out and firm up.
- Low Fat: Traditional melting cheeses like cheddar contain 30-40% fat, which helps create a smooth, even melt. Cottage cheese has far less fat, meaning it lacks the creamy consistency needed for melting.
How Curds React to Heat vs. How Melting Cheeses Behave
When you heat a traditional melting cheese:
The fat and protein soften and break down.
The structure becomes elastic, allowing it to stretch.
The cheese melts into a smooth consistency.
When you heat cottage cheese:
The curds hold their shape instead of breaking down.
The whey separates, leaving a watery residue.
The texture becomes firmer rather than creamier.
Lack of Emulsifying Agents in Cottage Cheese
Cheeses that melt well contain emulsifiers, which help blend fat and moisture into a smooth consistency. Processed cheeses, like American cheese, include emulsifiers to make them melt better. Since cottage cheese lacks emulsifiers, it does not melt like cheddar or mozzarella.
How Does Cottage Cheese React to Heat?
Softening vs. Melting: What to Expect
However, does cottage cheese melt like cheese in the traditional sense? No, but it does change when heated.
Softens: Cottage cheese can become slightly softer, but the curds remain intact.
Releases moisture: As it heats, whey separates, creating a watery consistency.
Doesn’t become gooey: Unlike cheddar or mozzarella, it won’t stretch or melt.
Texture Changes When Baked, Boiled, or Pan-Fried
Baking: Cottage cheese firms up when baked, making it a great addition to lasagnas and casseroles. It won’t melt, but it blends into the dish.
Boiling: When added to soups, cottage cheese holds its shape, offering a creamy texture without completely dissolving.
Pan-Frying: If cooked on a pan, cottage cheese browns slightly but retains its crumbly texture.
Storing & Refrigerating Cheese-Based Foods – Does Cottage Cheese Flatbread Need to Be Refrigerated?
Cooking with Cottage Cheese: Can You Make It Melt?
Since does cottage cheese melt like cheese the way cheddar does? No, but you can modify it to create a melt-like texture.
Blending for a Smoother Consistency
If you want a creamier texture, blend cottage cheese in a food processor before heating. This makes it easier to incorporate into sauces and soups without the curds separating.
Mixing with Other Cheeses to Create a Melt-Like Texture
Since does cottage cheese melt like cheese in its natural state? No, but mixing it with melting cheeses can help achieve a creamy texture. Try combining it with:
✔ Mozzarella (for stretchiness)
✔ Cheddar (for richness)
✔ Parmesan (for flavor)
This technique works well for dishes like baked pasta and stuffed shells.
Adding Fats and Emulsifiers for a Creamier Result
Since cottage cheese does not melt like cheese, adding a fat source like butter, heavy cream, or olive oil can help create a smoother consistency. This works best when making cheese sauces or dips.
Cottage Cheese in Cooking – Does Cottage Cheese Melt Like Cheese?
Recipes That Use Cottage Cheese Without Melting
Even though does cottage cheese melt like cheese traditionally? No, but it’s a fantastic ingredient for various dishes.
Cottage Cheese in Pasta and Baked Dishes
- Lasagna: Instead of ricotta, cottage cheese adds a creamy element without melting.
- Stuffed Shells: Mix it with mozzarella for a richer texture.
- Mac and Cheese: Blend it into the sauce for extra protein.
Using It in Creamy Sauces and Soups
- Tomato Soup: Stir blended cottage cheese for a velvety finish.
- Alfredo Sauce: Combine it with Parmesan for a lighter alternative.
- Chili: Add cottage cheese for a protein boost.
Cottage Cheese as a Ricotta Substitute
If you’re out of ricotta, cottage cheese works well in:
Cheesecake for a lighter texture.
Pancakes for extra fluffiness.
Dips like a spinach-artichoke dip.
Cottage Cheese in Cooking – Does Cottage Cheese Melt Like Cheese?
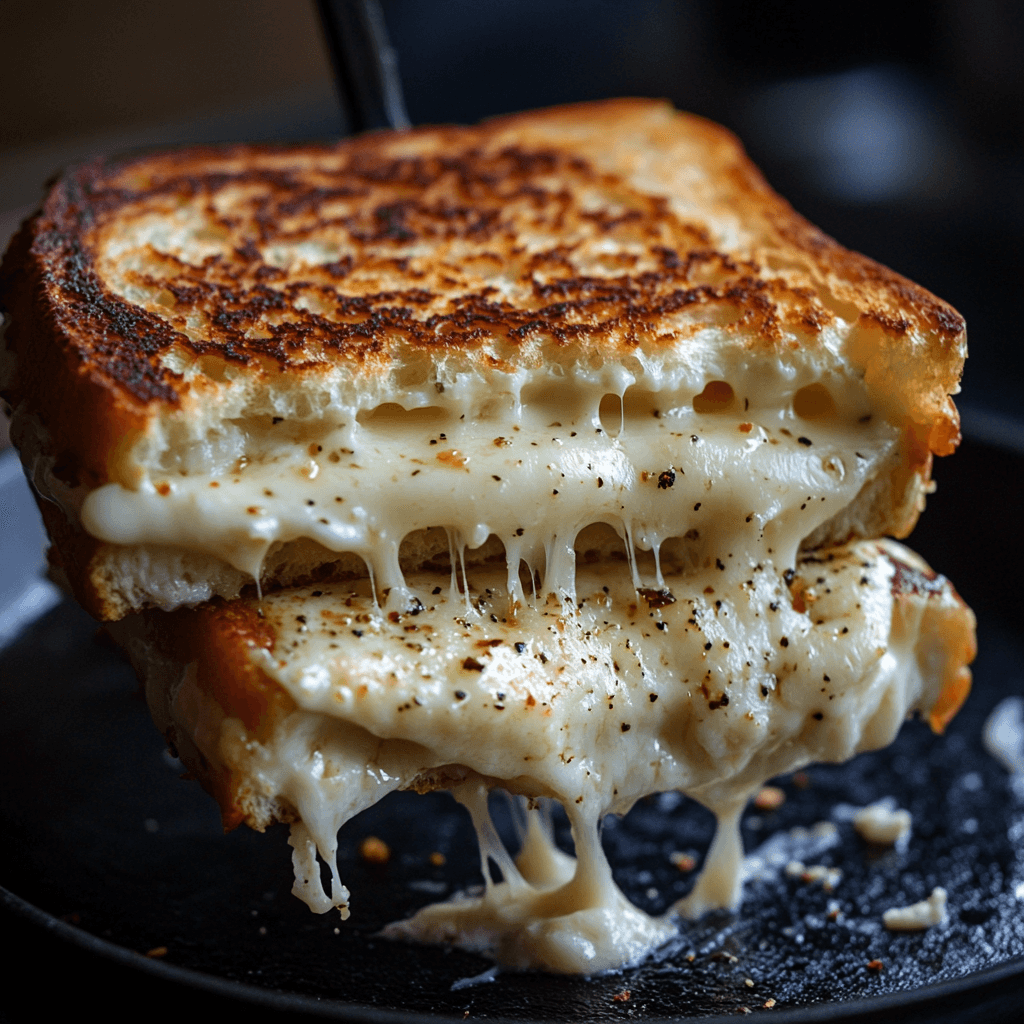
Does Cottage Cheese Melt Like Cheese in Specific Dishes?
Many home cooks wonder, “Does cottage cheese melt like cheese?” in dishes like lasagna, casseroles, or grilled cheese. While it doesn’t melt in the traditional sense, it softens and blends well when used correctly in recipes.
How Does Cottage Cheese Melt Like Cheese in Lasagna, Casseroles, and Grilled Cheese?
Lasagna: Many recipes use cottage cheese as a substitute for ricotta. When baked, it becomes creamy but does not melt like cheese such as mozzarella or cheddar. Instead, it holds its texture, making it a great option for a lighter, protein-rich lasagna.
Casseroles: Cottage cheese blends well in casseroles, adding moisture and a mild, tangy flavor. However, unlike cheeses that create a gooey consistency, it retains its curds and does not form a melted layer on top.
Grilled Cheese: If you’re wondering, “Does cottage cheese melt like cheese in a grilled cheese sandwich?”, the answer is no. Cottage cheese lacks the fat needed to create a smooth, melted texture, so it’s best to mix it with a melting cheese or use it as a spread inside the sandwich rather than as the primary cheese.
Using Cheese Alternatives in Cooking – Best Corn Casserole Recipe: The Ultimate Guide
Best Ways to Use Cottage Cheese When It Doesn’t Melt Like Cheese
If you want to use cottage cheese in dishes without expecting does cottage cheese melt like cheese, here are some effective techniques:
- Blend cottage cheese to create a creamy consistency for sauces or soups.
- Mix it with traditional melting cheeses like mozzarella or cheddar.
- Use it in baking where melting isn’t required, such as muffins or pancakes.
- Stir it into scrambled eggs for a protein boost.
Storing & Refrigerating Cheese-Based Foods – Does Cottage Cheese Flatbread Need to Be Refrigerated?
Why Some Recipes Combine Cottage Cheese with Melting Cheeses
Since cottage cheese does not melt like cheese, many recipes combine it with other cheeses to create a balance of creaminess and stretchiness. For example:
Lasagna: Blending cottage cheese with mozzarella creates a smoother texture.
Mac and Cheese: Mixing it with cheddar adds richness and creaminess.
Pizza Toppings: Some recipes mix cottage cheese with Parmesan or feta for extra creaminess without a melted layer.
Cottage Cheese in Cooking – Does Cottage Cheese Melt Like Cheese?
Best Substitutes When You Need a Melting Cheese
Since cottage cheese does not melt like cheese, you might need alternatives when a gooey, melted texture is required.
Ricotta, Cream Cheese, Mascarpone, and Their Melting Properties
Ricotta: Similar to cottage cheese but with a smoother texture, ricotta softens but does not melt. It works well in lasagna, pasta dishes, and spreads.
Cream Cheese: Creamy and spreadable, cream cheese melts into sauces but does not create a stretchy texture like cheddar or mozzarella.
Mascarpone: A rich, smooth cheese often used in Italian dishes, mascarpone adds creaminess but does not stretch like melting cheeses.
Using Cheese Alternatives in Cooking – Best Corn Casserole Recipe: The Ultimate Guide
How to Make Cottage Cheese Act More Like a Melting Cheese
Even though does cottage cheese melt like cheese, the answer is no, there are ways to modify it for a creamier texture:
Blend cottage cheese into a smooth sauce to help it integrate better into dishes.
Combine it with melting cheeses like mozzarella or cheddar for a richer consistency.
Use it in stuffed pasta mixed with Parmesan to enhance both flavor and texture.
While the question “does cottage cheese melt like cheese?” is often asked, it’s important to remember that although it won’t create a gooey, stretchy effect, it can still contribute creaminess and protein to a variety of dishes.
Choosing the Best Cheese for a Melted Effect
If your goal is a gooey, stretchy texture, the best cheeses include, but does cottage cheese melt like cheese in the same way? No, so consider these alternatives:
- Mozzarella (for stretchiness)
- Cheddar (for creaminess)
- Gouda (for richness)
- Swiss (for a nutty flavor)
Cheese Substitutes & Recipe Adjustments – Corn Casserole Without Jiffy: A Complete Guide
Common Misconceptions About Cottage Cheese Melting
Many people believe that does cottage cheese melt like cheese under certain conditions, but this is often due to misleading claims or confusion with blending techniques.
Why Do Some People Think Cottage Cheese Melts Like Cheese?
Blended cottage cheese appears smoother, leading some to believe it melts like a sauce. However, blending only breaks down the curds, it does not change its melting properties.
Some recipes combine cottage cheese with melting cheeses, making it seem as though the cottage cheese itself is melting.
When used in baked dishes, cottage cheese softens and integrates with other ingredients, giving the illusion of melting.
Misleading Claims About Melting Cottage Cheese
There are many claims online suggesting that cottage cheese melts when heated in specific ways. In reality:
- Cottage cheese does not melt like cheese because it lacks the fat and emulsifiers needed for a smooth, gooey consistency.
- Adding heat does not liquefy cottage cheese, it only makes it firmer.
- Blending cottage cheese does not change its structure, it only makes it creamier.
If you’re looking for a truly melting cheese, it’s better to choose a cheese designed for melting, such as cheddar or mozzarella.
Cheese Substitutes & Recipe Adjustments – Corn Casserole Without Jiffy: A Complete Guide
Conclusion: Does Cottage Cheese Melt Like Cheese? The Final Answer
So, does cottage cheese melt like cheese? The clear answer is no, but that doesn’t mean it lacks versatility in cooking. While it does not melt in the traditional sense, cottage cheese remains a protein-rich, creamy, and nutritious ingredient that can enhance various dishes. Its unique texture and mild flavor make it an excellent choice for blending into sauces, incorporating into casseroles, or using as a ricotta alternative.
Does cottage cheese melt like cheese? No, because it has high moisture, low fat, and lacks emulsifiers, which are necessary for a smooth, gooey melt.
Does cottage cheese melt like cheese in sauces? No, but blending it into a smooth consistency allows it to mix well with other ingredients, creating a creamy result.
Does cottage cheese melt like cheese in baking? No, but it softens, adds moisture, and blends well with other elements in dishes like lasagna and casseroles.
Does cottage cheese melt like cheese when heated? No, rather than melting, it firms up, releases moisture, and maintains its curds instead of becoming stretchy or gooey.
Even though cottage cheese does not melt like cheese, it remains a highly nutritious, protein-packed, and adaptable ingredient that can be used creatively in both savory and sweet recipes. Whether you blend it, mix it with melting cheeses, or use it in baked dishes, cottage cheese offers a rich, creamy texture without requiring melting.
For more expert tips on cooking with different cheeses, visit Allrecipes’ Guide to Cooking with Cheese.